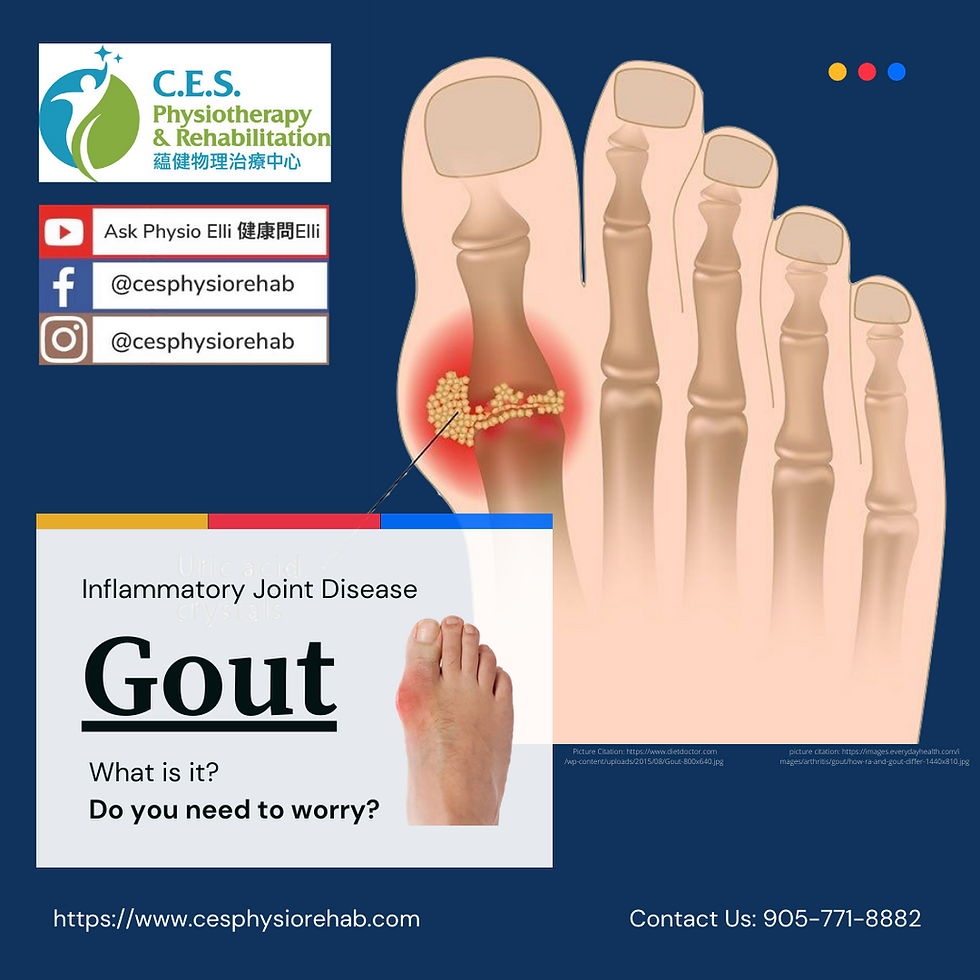
Gout is a type of arthritis. It is an inflammation of the joint and characterized by monosodium urate (MSU) crystals deposition in the joint. The main cause of gout is high uric acid (hyperuricemia) in the body.
The risk factors of gout include old age, male sex (2 to 6 times more in male vs female), obesity, purine diet, high alcohol consumption, some medications, genetics, and chronic diseases such as hypertension, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, congestive heart failure, and heart attack.
Diet that rich in purine is also one of the causes of gout. Consumption of food such as seafood, animal organs, red meat (pork, beef), alcohol, sweetened beverages, sodas, and high fructose corn syrup could increase the chance of one developing gout.
Presentation:
The most involved joint is the first metatarsophalangeal joint (big toe). The hand, ankle, knee, and other joints can also be affected sometimes. When it is during acute flare up, the pain is usually severe and has a quick onset, the joint will have local inflammation and appear red, swollen, and warm.
Physical examination, history taking, lab testing, arthrocentesis (joint fluid analysis) can all help diagnose gout.
Treatment:
The main goal of treatment is to reduce inflammation, pain, and other symptoms. The long-term goal is to reduce the level of uric acid and avoid subsequent flare-ups. Pharmacological interventions include NSAIDs (e.g. naproxen), or glucocorticoids could help fight the inflammation. Some other drugs act by either inhibiting the synthesis or increasing the clearance of uric acid. Be sure to consult with your pharmacist before taking any medications.
There are also many other non-pharmacological interventions for gout. Diet modification includes reducing red meat intake, alcohol consumptions, seafood, and sweetened soft drinks can help manage the disease. Weight loss and adequate hydration is also very important in terms of treatment.
Generally, health care professionals such as primary care physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistant, pharmacist, dietitian, specialists could be involved in the treatment process.
In terms of physiotherapy, your physiotherapist can examine the affected joint and the surrounding tissues and reduce inflammation and pain through the proper use of different physical modalities. He/she can also ensure you retain your physical ability when recovering from the disease.
Hope this short introduction of Gout can help you recognize gout when you see one!
Reference: Fenando, A., & Widrich, J. (2019). Gout (podagra).





.png)

Comments